Profit Margin Calculator 101: Formulas, Tips, and Examples
How profitable is your business, really? Do you know how much of your revenue is actually turning into profit? Are you struggling to determine where to focus your efforts to gain profitability?
The key to unlocking your financial success lies in one simple metric: profit margin.
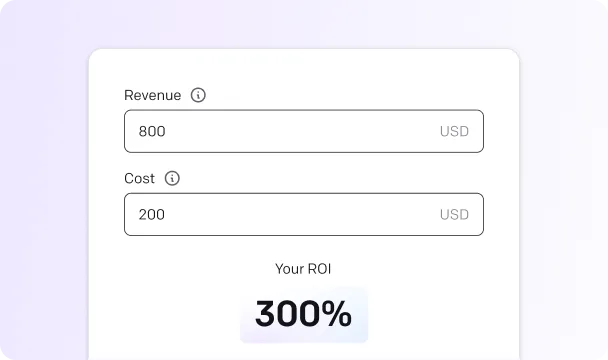
Profit margin calculator
Your profit margin
Table of contents
Every business, no matter its size, needs to understand its profit margins clearly to stay competitive and efficient.

Your profit margin is more than just a number. It’s a powerful indicator of your business's financial health. It shows how well you manage costs, pricing, and overall operational efficiency.
Here, you'll find the formulas you need to calculate your profit margin, share tips for improving it, and give you examples to make things crystal clear.
Whether you're new to the concept or need a refresher, you can make smarter, data-driven decisions impacting your bottom line.
Ready to take control of your finances?
Let's dive inWhat is the profit margin?
Profit margin measures how much of every dollar earned turns into profit. Think of it as the percentage of revenue left after covering specific costs. It’s a simple way to understand your business's profitability at different levels.
To fully understand it, here are a few essential terms to consider:
- Cost: These are the expenses involved in creating or delivering your product or service. Examples include materials, labor, and overhead costs.
- Margin: The difference between the selling price and the production cost. It’s the "cushion" your business has after covering costs.
- Revenue: The total income generated from selling goods or services. This doesn’t account for any costs yet.
- Profit: What’s left after subtracting all expenses (costs) from the revenue.
Now, why is profit margin important? It reveals how efficiently a business turns revenue into profit. Profit margins help identify areas for cost optimization, guide pricing strategies, and serve as benchmarks for comparing performance against competitors or industry standards.
For small businesses, healthy margins ensure sustainability, while for larger ones, they indicate operational efficiency and scalability. Regularly tracking your profit margins gives you actionable insights that drive better decisions, improve profitability, and ensure long-term success.
Types of profit margins
You can easily calculate profit margin after analyzing the key components involved. Let’s break down the main types: gross, operating, and net profit margins.
| Gross Profit Margin | Operating Profit Margin | Net Profit Margin | |
|---|---|---|---|
| purpose | Measures production efficiency | Evaluates the profitability of core business activities | Assesses total profitability after all expenses |
| usefulness | Manufacturing, retail businesses | Service industries, companies with high operating costs | All businesses, provides a complete financial picture |
| includes | Cost of goods sold (COGS) | COGS + operating expenses | All expenses (COGS, operating expenses, taxes, interest) |
| excludes | Operating costs, taxes, interest | Taxes and interest | None |
| key metric for | Product-based businesses | Operational efficiency and cost management | Overall business health and profitability |
| calculator | Calculate | Calculate | Calculate |
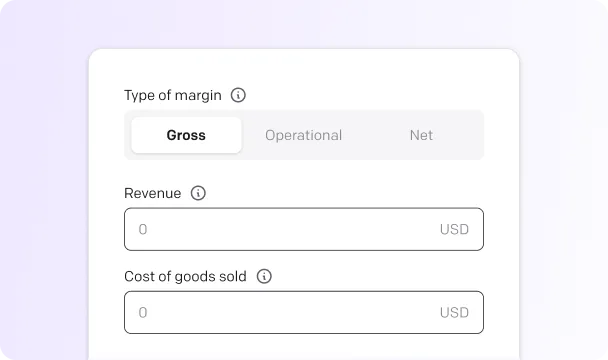
Gross profit margin
Gross profit margin measures the efficiency of your production process. It calculates the percentage of revenue left after subtracting the direct costs of producing goods or services. This margin doesn’t account for operating expenses like rent, salaries, or taxes, as it focuses solely on production efficiency.
Gross profit margin calculator
Your profit margin
GPM - Gross profit margin
R - Revenue
COGS - Cost of goods sold
The gross margin percentage indicates how efficiently your business produces goods or delivers services. A high margin suggests strong cost control or premium pricing strategies, while a low margin may signal rising production costs or poor pricing.
Example:
If your business earns $50,000 in revenue and spends $30,000 on production costs (COGS), your gross profit is $20,000, meaning 40% of your revenue remains after covering production expenses. A 40% gross profit margin means that 40 cents remain after covering production costs for every dollar earned.
Operating profit margin
Operating profit margin measures the profitability of a business’s core operations by considering operating expenses, such as rent, utilities, salaries, and production costs, but excluding taxes and interest. It shows how efficiently a company’s day-to-day activities generate profit before accounting for financing or tax obligations.
Operating profit margin calculator
Your profit margin
OPM - Operating profit margin
OI - Operating income
R - Revenue
Example:
Let’s say your business generates $50,000 in revenue and incurs $40,000 in operating expenses, which include COGS, salaries, rent, and utilities.
- Operating income = Revenue−operating expenses = $50,000 − $40,000 = $10,000
- Operating profit margin = Operating income/Revenue × 100 = $10,000 / $50,000 × 100 = 20%
A 20% operating profit margin means that for every dollar of revenue, 20 cents remain after covering the costs of running your core business activities.
The operating profit margin reflects how effectively your business manages its operating expenses relative to revenue. A high margin indicates strong profitability from core operations, while a low margin may signal inefficiencies or high overhead costs.
Net profit margin
Net profit margin is the most comprehensive measure of profitability. It calculates the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after accounting for all expenses, including COGS, operating expenses, taxes, interest, and one-time costs. This margin reflects the final financial outcome of your business operations.
Net profit margin calculator
Your profit margin
NPM - Net profit margin
NI - Net income
R - Revenue
Net profit margin shows how much of every dollar earned is kept as profit. It’s a critical measure of overall profitability and financial health. A low net margin might indicate excessive costs, high tax burdens, or inefficiencies across the board.
Example:
If your business generates $50,000 in revenue and incurs $45,000 in total expenses, your net income is $5,000. This results in a 10% net profit margin, meaning 10 cents of every dollar earned is kept as profit after covering all costs.
Turn clicks into revenue
Join your online presence with our trusted communication products.

In this partnership, I was simply looking for new streams of revenue. A great thing is that I also found lots of co-marketing opportunities and amazing support.
Syed Balkhi, WPBeginner
Explore our set of text-based tools
Profit Margin Calculator
Instantly check how much you’re really making on each sale.

JSON | CSV Converter
Enjoy best-in-class support to help you succeed — our team is here to assist you and your clients, anytime.

Regex Builder
A regex testing tool lets users debug regular expressions with real-time feedback.

Language Detector
Use free language identifier to detect the language of a text document or file.

Text to Speech Generator
Convert text to speech online to enjoy natural-sounding voices and high-quality audio files.
What is a good profit margin?
Profit margins can vary widely depending on the industry, so what's considered a "good" margin can differ from one sector to another. While a typical benchmark scale might categorize a 5% margin as low, 10% as average, and 20% as strong, these figures are not universal.
Industry variations play a significant role in defining what constitutes a healthy profit margin. For example, a retail business may have a profit margin significantly lower than that of an oil and gas company due to differences in operating costs and business models. Therefore, comparing profit margins across industries may not always be meaningful.
Studies analyzing profit margins by industry further illustrate these differences. Research by New York University revealed a wide range of net profit margins across sectors, with some industries showing margins as low as -29% and others reaching 33%. In their study, the hotel and gaming industry had an average margin of -28.56%, while banks had a healthy 32.61% margin.
Ultimately, what counts as a strong profit margin depends on the nature of the industry and how effectively a company manages its operations.

Let's become Partners!
We have excellent communication products, you have your audience. Let’s conquer the market together.
Become our PartnerHow to improve your profit margins
Improving your profit margin doesn't always require a drastic overhaul. Sometimes, small changes can make a big difference. Here are some tips that can help you boost your profitability:
1. Reduce operational inefficiencies
Start by taking a close look at your current operations. Are there processes that could be streamlined or eliminated? Reducing inefficiencies in production, distribution, or administrative tasks can help lower your costs. For example, automating repetitive tasks, improving inventory management, or reducing waste can free up resources and reduce overhead.
One way to do this is to incorporate tools like HelpDesk. By centralizing customer support, automating common tasks, and improving response times, you can significantly reduce labor costs.
2. Optimize pricing strategies
You might be underpricing your products or services. Carefully evaluate your pricing model and consider adjusting it to better reflect the value you offer. That doesn't necessarily mean raising prices across the board, but strategically increasing prices on high-demand or high-margin products.
You could also explore bundling or tiered pricing models that encourage customers to spend more while adding value.
3. Negotiate with suppliers to lower costs
Your suppliers are a major part of your cost structure. Negotiate better deals with them through bulk buying, longer-term contracts, or switching to alternative suppliers offering more competitive pricing. Even small savings on raw materials or services can significantly improve your margins over time.
4. Focus on high-profit margin products
Not all products or services are created equal when it comes to profitability. Identify the high-margin items in your portfolio and find ways to sell more of them. You might offer promotions or highlight these products more in your marketing material. The more you can focus on what generates higher profits, the better your overall profit percentage will be.
5. Build customer loyalty
It's often more expensive to acquire new customers than it is to retain existing ones. Building customer loyalty boosts sales and reduces the costs associated with marketing and customer acquisition. Loyal customers are more likely to repeat purchases, recommend your business to others, and spend more over time.
Offering loyalty programs, excellent customer support, and personalized experiences can help you keep your customers returning and increase your lifetime customer value.
1. Reduce operational inefficiencies
Start by taking a close look at your current operations. Are there processes that could be streamlined or eliminated? Reducing inefficiencies in production, distribution, or administrative tasks can help lower your costs. For example, automating repetitive tasks, improving inventory management, or reducing waste can free up resources and reduce overhead.
One way to do this is to incorporate tools like HelpDesk. By centralizing customer support, automating common tasks, and improving response times, you can significantly reduce labor costs.
3. Negotiate with suppliers to lower costs
Your suppliers are a major part of your cost structure. Negotiate better deals with them through bulk buying, longer-term contracts, or switching to alternative suppliers offering more competitive pricing. Even small savings on raw materials or services can significantly improve your margins over time.
5. Build customer loyalty
It's often more expensive to acquire new customers than it is to retain existing ones. Building customer loyalty boosts sales and reduces the costs associated with marketing and customer acquisition. Loyal customers are more likely to repeat purchases, recommend your business to others, and spend more over time.
Offering loyalty programs, excellent customer support, and personalized experiences can help you keep your customers returning and increase your lifetime customer value.
2. Optimize pricing strategies
You might be underpricing your products or services. Carefully evaluate your pricing model and consider adjusting it to better reflect the value you offer. That doesn't necessarily mean raising prices across the board, but strategically increasing prices on high-demand or high-margin products.
You could also explore bundling or tiered pricing models that encourage customers to spend more while adding value.
4. Focus on high-profit margin products
Not all products or services are created equal when it comes to profitability. Identify the high-margin items in your portfolio and find ways to sell more of them. You might offer promotions or highlight these products more in your marketing material. The more you can focus on what generates higher profits, the better your overall profit percentage will be.
Join one of the highest-paying programs
our top partner earned over
$4,100,000Make big bucks with us and change your business for the better.
Become our PartnerConclusion
Profit margin calculations help you gauge your current financial health and guide you toward smarter decisions that lead to growth.
Understanding your profit margin is essential for running a successful business, regardless of size. Using the formulas we’ve discussed and implementing practical strategies like optimizing pricing and reducing costs can give your business a real boost.
Slawomir Pawlak, Product Marketing Manager, Text
Remember, even small adjustments can greatly impact your bottom line. So, monitor those numbers, track your progress, and adjust as needed. You got this!

about the author
Slawomir Pawlak
I stumbled into the world of marketing by chance, but ended up loving it and have been working in the industry for 10 years. I have experience in various marketing roles, from agencies to software companies to startups. My expertise lies in B2B technical marketing, but I believe that all marketing is mainly human-to-human.
Read full biotext partners
Become our partner and maximize your profit margin
We have excellent communication products, you have your audience. Let’s conquer the market together.
20+
years on the market
800+
leads referred to partners last year
41,000+
customers using Text products

What's in it for you?
Marketplace exposure to 37,000+ clients.
Grow your business with exposure to a global customer base looking for top-tier solutions and services.
Earn 20% recurring revenue — every month.
Start earning a predictable monthly income with every client you bring on board.
Co-marketing opportunities.
Gain access to a wealth of resources, including marketing materials, training, and support, to help you succeed.
Personal onboarding and free account.
You’ll get personal onboarding and a free product account to showcase our software.
24/7 support from our expert team.
Enjoy best-in-class support to help you succeed — our team is here to assist you and your clients, anytime.
Exclusive product discounts for your clients.
Offer your clients the best deals and help them save on essential tools.

With ChatBot and LiveChat, we're qualifying so many more leads than we were ever doing with previous campaigns.
Brandon Klayman, Conscious Commerce
$50,000 in deals and a 379% increase in website sales
Read success storyFAQ
- Gross profit margin — revenue minus direct production costs.
- Operating profit margin — revenue minus production and operating expenses.
- Net profit margin — revenue minus all expenses, including taxes and interest.
You can use the calculator above to find each one — just enter the right numbers!